Set Up Google Search Console | Know More about Domain Property and URL Prefix Property | Digital Marketing Tutorial
What is Google Search Console?
Google Search Console, formerly known as Google Webmaster Tools, is a free web service provided by Google that allows website owners, webmasters, and SEO professionals to monitor and manage their website's presence in Google search results. It offers a range of tools and reports that provide valuable insights into how a website is performing in Google's search engine and helps optimize its visibility and performance.
Key Features of Google Search Console:
- Search Performance Analysis: Google Search Console provides data and reports on how a website is performing in Google search results. It offers information about the keywords and phrases that drive organic traffic, the number of impressions and clicks, click-through rates (CTRs), and average position in search results. This data helps webmasters analyze and improve their website's visibility and user engagement.
- Indexing Status: The Index Coverage report in Search Console provides information about the pages on a website that are indexed by Google. It highlights any indexing errors or issues that might prevent certain pages from being included in search results. Webmasters can use this information to identify and fix any problems that could affect the visibility of their website in search results.
- Sitemap Submission: Webmasters can submit a sitemap of their website to Google Search Console. A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on a website, helping search engines understand its structure and content. By submitting a sitemap, webmasters can ensure that Google crawls and indexes their web pages more efficiently.
- Mobile Usability: Google Search Console provides a Mobile Usability report that identifies any issues or errors on a website that could affect its performance on mobile devices. With the growing importance of mobile-friendly websites, this report helps webmasters optimize their site's mobile user experience and ensure compatibility across different devices and screen sizes.
- URL Inspection Tool: This tool allows webmasters to inspect specific URLs on their website and see how Google crawls and renders them. It provides information about whether a page is indexed, any crawl errors encountered, and how the page appears in Google search results. This tool is helpful for troubleshooting and diagnosing issues with individual pages.
- Security Issues and Manual Actions: Google Search Console alerts webmasters if their website has any security issues, such as malware or hacked content. It also notifies them if the website has received a manual action from Google, which is a penalty imposed for violating Google's Webmaster Guidelines. These notifications help webmasters take immediate action to address security concerns and rectify any policy violations.
- Links and External Resources: Webmasters can view the links pointing to their websites using the Links report. It provides information on the websites that link to theirs, the pages on their website with the most links, and the anchor text used in the links. This data helps identify link-building opportunities, assess the quality and relevance of inbound links, and monitor the impact of link-building efforts.
How to Set Up Google Search Console
Setting up Google Search Console is a straightforward process. Follow the steps below to get started:
- Create a Google Account: If you don't have a Google Account, create one by visiting accounts.google.com/signup. Ensure that you use an account that is associated with your website or business.
- Access Google Search Console: Visit the Google Search Console website at search.google.com/search-console. Sign in using your Google Account credentials.
- Add Property: On the Google Search Console dashboard, click on the "Add Property" button. Enter the URL of your website (e.g., "https://www.example.com") in the provided field. Click "Continue" to proceed.
- Verify Ownership: Google requires you to verify that you own the website before granting access to Search Console data. There are several verification methods available:
- Recommended Method: HTML File Upload: Download the HTML verification file provided by Google. Upload this file to the root directory of your website using an FTP client or file manager provided by your hosting provider. Once uploaded, click on the "Verify" button in Search Console.
- Alternative Methods: If you are unable to upload an HTML file, Google offers alternative verification methods. These include adding a meta tag to your website's homepage, verifying via Google Analytics, or using DNS verification.
- Confirm Verification: Once you've completed the verification process, Google will confirm the successful verification. You can now access the Search Console dashboard for your website.
- Explore Search Console Features: Familiarize yourself with the various features and reports available in Google Search Console. These include the Performance report, Index Coverage report, Mobile Usability report, URL Inspection tool, and more. Each feature provides valuable insights and data about your website's performance in Google search results.
- Submit a Sitemap: To ensure that Google indexes your website accurately, submit a sitemap. Generate a sitemap using a sitemap generator tool or a plugin if you're using a content management system (CMS) like WordPress. Once generated, submit the sitemap through the "Sitemaps" section in the Search Console dashboard.
- Set Up Search Console Preferences: Customize your Search Console settings by clicking on the gear icon in the top-right corner of the dashboard. Here, you can specify preferences such as email notifications, preferred domain (www or non-www), and user management.
- Start Monitoring and Optimizing: With Google Search Console set up, you can now start monitoring your website's performance, identifying issues, and optimizing for better search engine visibility. Regularly check the reports, review crawl errors, address indexing issues, and leverage the available tools to enhance your website's presence in Google search results.
In short, setting up Google Search Console is an essential step for website owners and webmasters to monitor and optimize their website's performance in Google search results. By following the steps outlined above, you can establish a connection between your website and Search Console, gain access to valuable data and reports, and leverage the insights to improve your website's visibility, indexing, and overall search engine presence.
In the digital age, websites play a vital role in establishing an online presence for businesses, organizations, and individuals. Ensuring a website's accessibility and security are crucial aspects of website development and management. Two fundamental properties that contribute to achieving these objectives are the Domain Property and URL Prefix Property. This article aims to delve into these properties, explaining their significance and how they enhance website accessibility and security.
Domain Property:
The Domain Property refers to the unique name that identifies a website on the internet. It serves as the website's address and is an essential part of its URL. For instance, in the URL "https://www.example.com," the domain property is "example.com." The domain property acts as an identifier, allowing users to access a website directly by typing it into a web browser
How to Add a Domain Property
Adding a domain property in Google Search Console allows you to monitor the performance and manage the settings for an entire domain, including all its subdomains. To add a domain property to Google Search Console, follow these steps:
- Sign in to Google Search Console: Visit the Google Search Console website at search.google.com/search-console and sign in using your Google Account credentials
- Access the Property Menu: On the Search Console dashboard, click on the drop-down menu in the top-left corner (usually displaying the name of your existing property). From the menu, select "Add Property."
- Enter the Domain: In the "Domain" section, enter the domain name you want to add. For example, if you want to add "example.com" as your domain property, enter "example.com" without the "https://" or any specific page or subdomain.
- Verify Domain Ownership: Google requires you to verify that you own the domain before granting access to the Search Console data. Choose one of the available verification methods. The recommended method is usually the DNS TXT record:
- DNS TXT Record: Select this method, and Google will provide you with a unique TXT record to add to your domain's DNS settings. Access your domain registrar or DNS provider's settings, locate the DNS management section, and add the TXT record as instructed by Google. It may take some time for the DNS changes to propagate.
- Alternative Verification Methods: If the DNS TXT record method is not feasible, Google offers alternative methods such as HTML file upload, HTML tag, Google Analytics, or Google Tag Manager. Choose the method that works best for you and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Confirm Verification: Once you've completed the verification process, Google will confirm the successful verification of your domain ownership. You can now access the Search Console dashboard for your domain property.
- Set Up Preferred Version: After verifying your domain, you should specify the preferred version of your domain—either with the "www" prefix or without. To do this, click on the gear icon in the top-right corner of the dashboard, select "Site Settings," and choose the preferred version under the "Preferred domain" section.
- Configure Settings: Customize your domain property settings as needed. This includes specifying email preferences, user management, and other settings to suit your requirements. Explore the various options available in the Search Console settings.
- Start Monitoring and Optimizing: With your domain property added to Google Search Console, you can now monitor the performance, index coverage, and other important aspects of your entire domain and its subdomains. Utilize the available reports and tools to identify issues, optimize your website's search engine visibility, and improve overall performance.
By adding a domain property in Google Search Console, you gain a comprehensive view of your entire domain's performance and settings. Following the steps outlined above will help you establish a connection between your domain and Search Console, verify ownership, and enable you to monitor and optimize your website's presence in Google search results effectively. Remember to regularly check the reports, address any issues, and leverage the insights provided by Search Console to enhance your domain's visibility and performance.
Significance of Domain Property:
- Branding and Identity: The domain property plays a significant role in establishing a website's brand and identity. It allows businesses and organizations to choose a domain name that aligns with their brand, making it easily recognizable and memorable for users.
- Trust and Credibility: A well-chosen domain name can instil trust and credibility in users. When a website's domain property aligns with its content or purpose, users are more likely to perceive it as authentic and trustworthy, increasing the likelihood of engagement and conversion.
- SEO and Discoverability: Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is crucial for websites to appear prominently in search engine results. The domain property can impact SEO by including relevant keywords that are related to the website's content or industry. A well-optimized domain name can improve a website's discoverability and organic traffic.
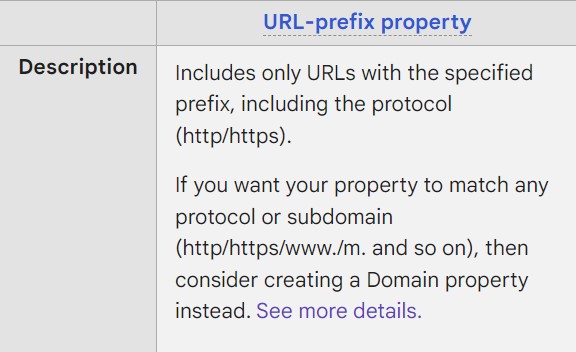
URL Prefix Property:
The URL Prefix Property refers to the characters preceding the domain property in a URL. These characters are used to specify the protocol or method by which the website should be accessed. The most common URL prefix properties include "http://" and "https://".
According to Google:
Significance of URL Prefix Property:
- Security: The URL prefix property is closely associated with website security. The "http://" prefix indicates a website that uses the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), while "https://" indicates a secure website that uses the Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). The latter provides encryption of data transmitted between the user's browser and the website, ensuring privacy and protection against unauthorized access or tampering.
- Trustworthiness: As internet users become increasingly aware of online security risks, they tend to trust websites with the "https://" prefix more than those with "http://". Secure websites display a padlock icon in the browser's address bar, assuring users that their connection is secure. This perception of trustworthiness can significantly impact user engagement, conversion rates, and overall website reputation.
- SEO and Ranking: Search engines, such as Google, have recognized the importance of website security in their ranking algorithms. Websites with an "https://" prefix are more likely to rank higher in search results, providing an added incentive for website owners to implement SSL certificates and ensure secure connections.
The Domain Property and URL Prefix Property are integral components of a website's address and play a crucial role in enhancing website accessibility and security. The domain property establishes a website's identity and brand, while the URL prefix property ensures secure and encrypted connections. By understanding the significance of these properties, website owners and developers can optimize their websites for improved user experience, trust, search engine visibility, and overall online success.
Owners, Users, and Permissions
Google Search Console allows website owners to grant different levels of access and permissions to various individuals or groups. These roles include owners, users, and permissions. Let's explore each of these in more detail:
- Owners: Owners have full control and management authority over a property in Google Search Console. They have the highest level of access and can perform tasks such as adding and removing users, managing settings, and viewing all data and reports for the property. Owners have the ability to make critical changes to the website's configuration and should be trusted individuals or entities responsible for the website's overall management.
- Users: Users are individuals or groups who are granted access to specific properties within Google Search Console. They have more restricted permissions compared to owners and can be assigned different roles and access levels based on their responsibilities and requirements. Users can access data, reports, and specific features according to the permissions granted by the owner.
- Permissions: Permissions define the level of access and actions that can be performed by users. Google Search Console offers the following permission levels:
- Full: Users with full permissions have access to all data and features within a property. They can view reports, make configuration changes, and manage settings.
- Restricted: Restricted users have limited access to certain data and features within a property. Owners can customize their access by choosing specific permissions for different actions or sections of the Search Console.
- Read-only: Read-only users can view data and reports but cannot make any changes or modifications. They have read-only access to the property's information.
- No access: Users with no access cannot view or interact with the property in Google Search Console.
Setting Up Users and Permissions:
Sign in to Google Search Console: Visit the Google Search Console website at search.google.com/search-console and sign in using your Google Account credentials.
- Access Property Settings: Select the property you want to manage, and click on the gear icon in the top-right corner of the dashboard to access the property's settings.
- Manage Users: In the settings menu, select "Users and permissions" or a similar option. Here, you can view the current list of users and their roles for the selected property.
- Add a User: To add a user, click on the "Add user" or a similar button. Enter the email address of the individual or group you want to grant access to. Choose the appropriate permission level (Full, Restricted, or Read-only) for the user.
- Remove or Modify User Access: To remove or modify a user's access, locate their email address in the user list and click on the corresponding options (e.g., Remove, Edit) next to their name. Make the necessary changes and save your modifications.
It's important to manage user access and permissions carefully to maintain the security and integrity of your website and its data. Grant access only to trusted individuals or groups and regularly review and update user permissions as needed.
Remember, the steps and options mentioned above are based on the information available up until my knowledge cutoff in September 2021. It's always advisable to refer to the official Google Search Console documentation for the most up-to-date instructions and guidelines regarding user management and permissions.
How to Add a Sitemap to Google Search Console
First, access Google Search Console.
Register for a Google Search Console account first.
Select the website you wish to submit a sitemap for in the top left corner after that. (In the event that you have many properties on the same account.)
Second, Visit the 'Sitemaps' Report.
A "Sitemaps" report may be found under "Indexing" in the left sidebar menu. Head there.
All of your sitemaps may be managed here. It is divided into two main sections:
“Add a new sitemap”
“Submitted sitemaps”
Let's focus on: Add a new sitemap
Third, Locate the sitemap's URL
Sitemaps can be divided into two categories: XML sitemaps and HTML sitemaps. Since HTML sitemaps are not utilised for SEO, this article will concentrate on XML sitemaps.
A few quick and easy ways to locate your XML sitemap:
- Try the most typical location. Your XML sitemap is probably going to be found at https://mypetstore.com/sitemap.xml.
- Put a search operator to use. You can locate your sitemap by searching Google for "site:mypetstore.com filetype:xml."
- Take a look at your robots.txt file. Possible links to your sitemap can be found in your robots.txt file, which can be found at https://mypetstore.com/robots.txt.
You must make an XML sitemap before adding any kind of sitemap to Google Search Console.
Fourth, Add a new sitemap.
The "Add a new sitemap" part of the "Sitemaps" report is now available for you to add your sitemap to.
Copy the URL, then click "Submit."
You'll notice a message stating that your sitemap submission was successful.
Your sitemap will eventually appear in the list of "Submitted sitemaps." It details the sitemap's submission date, its most recent read date, and the number of pages that Google found on the sitemap.
Additionally, it will let you know how your sitemap submission is progressing. There are no problems if the "Success" status is green.
If you observe a "Couldn't fetch" or "Has errors" status, you must rectify the problems according to the report's instructions.
Google Search Console Reports and Features
Google Search Console provides a range of reports and features that offer valuable insights into your website's performance, indexing, and visibility in Google search results. Let's explore some of the key reports and features available in Google Search Console:
Performance Report
Information about your website's performance on Google is available in the "Performance" report.
Here are some suggested metrics:
- Total clicks: The quantity of times visitors from the search results have clicked on your website.
- Total impressions: Impressions overall The frequency with which your site surfaced in search results
- Average CTR (click-through rate): how many out of every 100 impressions led to a click
- Average position: Your website's typical position in search results
From the sidebar navigation, select "Search results" to access these statistics for your website.
You may find a table that displays the searches, pages, nations, and devices that are bringing visitors to your site just below the graphic. Additionally, details on the page experience and the number of clicks you received by date.
Two suggestions for what to check for while examining your Google performance data are provided below:
Low CTR: If your sites are well-ranked yet receive few hits, you might want to explore improving your title tags and meta descriptions. Your pages will become more enticing to users as a result.
Missing keywords: Your website may lack sufficient helpful material addressing essential keywords if you don't rank for them. If so, you should refine your content strategy and create high-quality material that is targeted at the keywords you want to rank for.
You'll also see specialised reports for Discover and Google News if these two sources of traffic are used to visit your website.
Reports will look like:
URL Inspection Tool
You can examine the index status of a specific internet page using the "URL inspection" tool. And address any problems that might be stopping Google from indexing your page.
You can access the tool by clicking "URL inspection" in the navigation bar or the top bar.
Paste the complete URL in the inspect search box and hit enter to examine the index status of a certain page.
The following details will be included in the results:
- Index status: Google's indexing of the page is shown by its status as an index.
- Latest crawl: When Google last crawled the page, both the date and time
- Mobile usability: Whether the website satisfies Google's mobile-friendly requirements
- Structured data: Organising data Whether or if the page contains structured data (and whatever issues there may be)
In order to see how a page seems to Googlebot, you may also test live URLs using the tool.
Click "TEST LIVE URL" in the top-right corner of the screen to use.
Go to the results page and select "VIEW TESTED PAGE" > "SCREENSHOT."
The URL inspection tool can also be used to ask Google to index new pages on your website.
In the Inspect search box, paste the entire URL and hit enter. After that, select "REQUEST INDEXING."
This may accelerate the indexing process.
Page Indexing Report
The "Indexing" part contains the "Page indexing" report. It displays the pages that Google can find and index as well as any relevant problems.
For pages to show up in search results, they must be indexed. Therefore, it's crucial to prevent any indexation issues.
Select "Pages" from the sidebar's "Indexing" section.
Two tabs will be visible, one for indexed pages and the other for unindexed pages.
The number of indexed pages may have suddenly decreased, which could indicate a problem.
To see why your pages weren't indexed, scroll down.
Many factors can prevent some of your pages from being indexed.
For instance, it's possible that your pages are displaying "Not Found (404)" errors. Or perhaps you accidentally added the "noindex" tag.
You can pinpoint the issue with the aid of this report.
Click on an entry in the "Reason" column to enlarge it and learn more about a specific cause.
A list of pages that are impacted will appear.
At the very top is a link to a page that explains how to resolve the problem.
If you make any corrections, you can click "VALIDATE FIX" to let Google know that you did so. Hopefully, this will index the impacted pages.
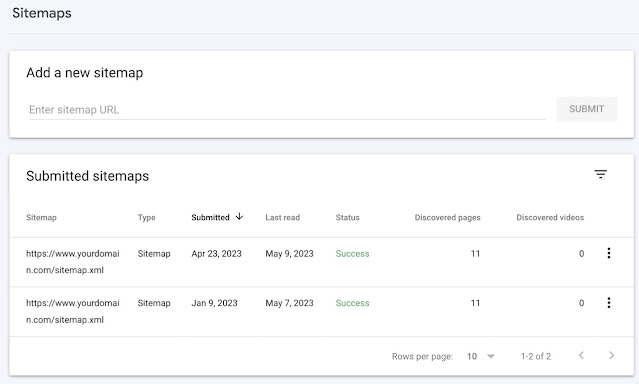
Sitemaps Report
The "Sitemaps" report shows the history of your sitemap submissions and notifies you of any errors.
Go to "Sitemaps" in the sidebar to see the report.
You'll discover the following details:
- URL: The address you provided while submitting your sitemap
- Type: The sitemap's format (XML, RSS, etc.)
- Submitted: The day you first delivered the sitemap
- Last read: the previous day Crawling the sitemap by Google
- Status: The state of the crawl, such as "Success," "Has errors," or "Couldn't fetch"
- Discovered pages: Pages that were found Google discovered a total of pages in the sitemap.
Make sure "Success" appears in the "Status" column. This indicates that your sitemap was correctly and successfully processed.
Here is a summary of unsuccessful statuses and advice on how to approach them:
- Has mistakes: Your sitemap has one or more mistakes. Examine the mentioned errors and read Google's tutorial to discover how to correct each one.
- Couldn’t fetch: Unable to fetch GSC was unable to get your sitemap. To explore the problems, return to the "URL inspection" tool and run a real URL test.
You can see a report for a given sitemap by clicking on the entry you submitted for a sitemap.
You may get your sitemap's "Page Indexing" report by clicking the "SEE PAGE INDEXING" button, which is indicated above.
The report informs you of the indexation status of each page in your sitemap.
Page Experience Report
Information regarding a website's performance in terms of user experience is available in the "Page Experience" report.
The following criteria are used to assess user experience:
- Core Web Vitals: Google's Core Web Vitals are a series of measurements that gauge how quickly, interactively, and visually stable webpage content loads.
- Mobile Usability: Whether a mobile user can access your website
- HTTPS: Whether the connection to your website is secure
The outcomes are divided into mobile:
Also, desktop:
The number of "Good URLs" as a percentage shows how many URLs give users the best possible page experience.
Examine each report to identify your shortcomings.
It is advised to consult a team member who is a developer to help you resolve Core Web Vitals problems. (Unless you have technical SEO skills.)
When the problem has been resolved, notify Google of the adjustment by selecting "VALIDATE FIX" in the error report's top section.
Enhancements Report
Google will display details on any structured data it finds on your website in the "Enhancements" report. and if there are any problems right now.
Google receives more information about your page via structured data. Google takes advantage of this data to produce rich SERP results. It might enhance the CTR for your pages.
The "Enhancements" section of the sidebar has a list of the many kinds of structured data that Google can identify.
For the complete report, click on a certain type. In this box, we choose "Breadcrumbs."
The report indicates "Invalid" items to let you know if there are any issues.
You should have 0 "Invalid" items. The affected pages won't show up in search results as rich results if there are any problems.
Manual Actions Report
In the event that a website violates Google's spam regulations, Google takes manual action.
In Google search results, websites with manual actions (or fines) may appear substantially lower or not at all.
This can result in a significant drop in traffic.
Visit the "Manual actions" report in Search Console to see if Google has taken manual action against your website.
If the report states "No issues detected," there is nothing you need to do.
However, if "Issues detected" appears in this report, you have a significant issue. And you must solve each problem right away.
In Google's manual actions report guide, you can find instructions on how to handle particular fines.
Links Report
You can keep track of your backlinks and external links using the "Links" report. Backlinks are links pointing to your website from other websites.
They also play a significant role in Google ranking.
Go to "Links" on the sidebar to view this report.
The total number of backlinks to your website is displayed at the top.
View your top linked pages—those that are receiving the most backlinks—under that.
Additionally, the top websites that connect to you.
Along with the most typical anchor text used when linking to you:
The "Links" report also reveals which pages on your website have the most links from other pages inside your own domain or internal links.
Internal links are crucial for SEO for two reasons in particular:
- They make it easier for consumers and spiders to traverse your website.
- They give authority to other pages on your website, which could improve their ranking.
A list of your internal links is located on the right of the report.
You may view your top linked pages as well as the overall number of internal connections.
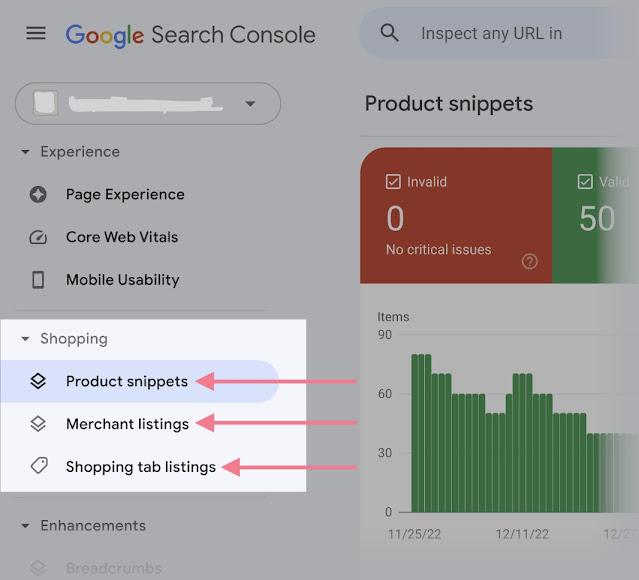
Shopping Report
For online shops and product review websites that have adopted product markup on their websites, see the "Shopping" report.
It displays information on the structured data issues pertaining to your goods.
Depending on the type of structured data Google discovers on your website, you may see a combination of the following reports:
- Product snippets: Snippets of products in search results with problems with structured data
- Merchant listings: Detects problems with structured data for free listings throughout Google.
- Shopping tab listings: Identifies problems with structured data for products that show up in the Shopping tab of Google Search results.
Use the sidebar to find the specific report.
You can also check for any "Invalid" entries.
If "Invalid" elements are present, Google won't display the impacted pages as rich results.
So check the report's "Invalid" elements to see what mistakes there are.
Use Google's Rich Results Test to verify your structured data code after you've fixed the problems.
The tool will inform you if your updated code is functional. Additionally, find out if your entry qualifies for a rich result.
AMP Report
A lightweight, quick-loading HTML framework is called AMP (formerly known as accelerated mobile sites).
Google generates a report in Search Console describing those pages when it discovers AMP on your website. additionally, any problems that stop Google from crawling the AMP sites.
Select "AMP" from the navigation sidebar to get the report.
In the summary report, your pages are divided into two groups:
- Valid pages: These pages can show up in search results because they don't have any AMP-related concerns.
- Invalid pages: Due to a number of difficulties, these pages are unable to appear in search results.
To view the list of problems with your AMP pages, scroll down.
In order for your AMP pages to start showing up in search results, fix each issue.
In this situation, contacting a developer is advised. Unless you are a specialist in this area.
Click "VALIDATE FIX" to request Google's confirmation of your fixes after you've resolved the problems.
In conclusion, Google Search Console offers a comprehensive set of reports and features that provide valuable insights and tools for website owners and webmasters. By leveraging these functionalities, you can gain a deeper understanding of your website's performance, indexing status, and visibility in Google search results. The Performance report allows you to analyze key metrics such as impressions, clicks, and CTR, helping you optimize your content and improve search rankings. The Coverage report helps identify indexing issues, errors, and warnings, enabling you to address them and ensure proper indexing of your pages. The URL Inspection tool provides in-depth information about specific URLs, aiding in troubleshooting and optimizing their indexing and visibility. The Mobile Usability report focuses on mobile-specific issues, ensuring a smooth user experience on mobile devices. The Links report helps you understand your website's linking patterns, identify high-quality backlinks, and address any spammy or low-quality links. The Core Web Vitals report highlights user experience metrics, allowing you to optimize loading, interactivity, and visual stability. The Sitemaps feature enables the submission and monitoring of your website's sitemap for efficient crawling and indexing. Lastly, the Security Issues report alerts you to any security-related problems that may affect your website's integrity and user trust. By regularly utilizing these reports and features, you can make data-driven decisions, address issues, and enhance your website's performance, visibility, and user experience in Google search results.





























Comments
Post a Comment